I’ve long held that if a problem can be solved by creating $1 trillion out of thin air and buying a raft of assets with that $1 trillion, then central banks will solve the problem by creating the $1 trillion out of thin air—nothing could be easier.
This is the lesson of the past eight years: if a problem can be solved by creating new money and buying assets, then central banks will solve that problem.
Problem: stock market is declining. Solution: create new money and buy, buy, buy stock index funds. Problem solved! Market stops falling and quickly rebounds as “central banks have our backs.”
Problem: interest rates are inhibiting lending and growth. Solution: create a few trillion units of currency and buy enough sovereign bonds to drop interest rates to near-zero.
Problem: nobody’s left who can afford to buy the new nosebleed-priced flats that underpin China’s miracle-grow economy. Solution: create new currency, lend it to local government agencies who then buy the empty flats.
Problem: stagnant employment and deflation. Solution: create a trillion in new currency, buy a trillion in new government bonds that then fund infrastructure projects, i.e. bridges to nowhere.
And so on. Any problem that can be solved by creating a few trillion out of thin air and buying assets will be solved. The mechanism to solve these problems—creating currency out of nothing—is like a perpetual motion machine: there are no intrinsic limits on the amount of new money that can created at near-zero interest, as the interest payments can be funded by new money.
Even better, the central bank (the Federal Reserve) buys Treasury bonds with the new currency that generate income, which is then returned to the Treasury: a perpetual-motion money machine!
The policy of creating trillions in new currency and buying trillions in assets has inflated an everything bubble, a bubble in all the asset classes being supported or purchased by central banks and their proxies.
Many observers wonder what, if anything, could pop the everything bubble.
This leads to an interesting question: what problems can’t be solved by creating another trillion and buying assets?
What Problems Can’t Be Solved by Creating Another Trillion and Buying Assets?
The past eight years have created the comforting illusion that essentially all problems in the modern era of globalized, centralized, debt-based, state-cartel capitalism in all its flavors (Chinese, Japanese, European, American, etc.) can be solved by creating as many trillions as are needed (whatever it takes) and buying assets or issuing guaranteed lines of credit with the new currency.
But there are some structural problems that can’t be solved by this mechanism. Some are primarily economic, some are primarily political-social, but all of them affect the entire system, not just the financial realm.
Inflation
We’re told that inflation—the loss of purchasing power of a currency—is near death and this greatly saddens the globe’s central bankers, who desperately need inflation to push wages higher and reduce the burden on debtors.
So let’s say, just as a thought experiment, that central banks get their much-desired inflation, but it runs hotter than their 2% annual target. Once inflation is embedded in expectations and the supply chain, printing another trillion and using it to buy stocks, bonds, empty flats, etc. won’t make inflation go away. Rather, the inflation in asset valuations generated by endless central bank buying if assets ends up feeding real-world inflation as all this new currency doesn’t actually produce more goods and services; it simply expands the supply of currency sloshing around the world looking for speculative yield.
The chorus of voices advocating for Universal Basic Income (UBI) is growing, and central banks will increasingly be pressured to issue new currency to fund UBI and its equivalents—what’s known as helicopter money, as the central bank issues currency that then funds deficit spending, i.e. the government dropping cash into the real economy.
Helicopter money comes in a variety of forms: debt forgiveness, negative tax rates (i.e. tax rebates to those who owe no income taxes), and cash stipends such as UBI. In every case, this helicopter money doesn’t expand the supply of goods and services; all it does is expand the funds available for consumption.
While China may be able to export deflation in goods that are tradable, that is, commoditized goods that can be made anywhere and shipped to markets elsewhere, nontradable goods and services such as local government services, housing, groceries, fast food, most healthcare services, haircuts, education, etc.—the bulk of the real economy—soar in price as the supply of money expands faster than the supply of these goods and services.
This is why inflation is already running extremely hot in nontradable sectors (which are often dominated, funded or controlled by the public sector/government), while deflation is still visible in tradable goods such as TVs, software, etc. I covered real-world inflation rates in The Burrito Index: Consumer Prices Have Soared 160% Since 2001 (August 1, 2016))
Much of the real-world inflation in sectors such as healthcare is invisible to protected classes because it’s being absorbed by employers and the government, a topic I covered in Inflation Isn't Evenly Distributed: The Protected Are Fine, the Unprotected Are Impoverished Debt-Serfs (May 25, 2017)
Real-world inflation is also distorted by hedonics and substitution, tricks that lower the official rate of inflation but don’t change the reality that the average prices paid for vehicles have risen substantially, despite the official claim that vehicle prices have been flatlined for years, a topic I addressed in About Those "Hedonic Adjustments" to Inflation: Ignoring the Systemic Decline in Quality, Utility, Durability and Service (October 11, 2017)
Be Careful What You Wish For: Inflation Is Much Higher Than Advertised (October 5, 2017)
As political pressure on central banks mounts to fund QE for the people, QE for Main Street, etc., that is, helicopter money in one form or another, the introduction of new currency into the real economy has the potential to make real-world inflation undeniable.
Once inflation is undeniably in the 5% to 7% range, who will be willing to buy a negative-interest rate bond, or a bond paying 1%?
Another potential engine of inflation that’s widely discounted is global shortages of key commodities such as oil, grain, fresh water, etc. The global economy has come to view cheap, abundant commodities as the natural and permanent state of affairs, but history tells us that abundance and low prices are not permanent. Since essential commodities are integral to the global supply chain, any price increases due to scarcity or supply disruption quickly feed inflation into the entire supply chain.
Inflation is a problem that creating another trillion won’t solve; creating and distributing another trillion or two will actually make the problem worse.
Rising Social Disorder Due to Soaring Wealth-Income Inequality
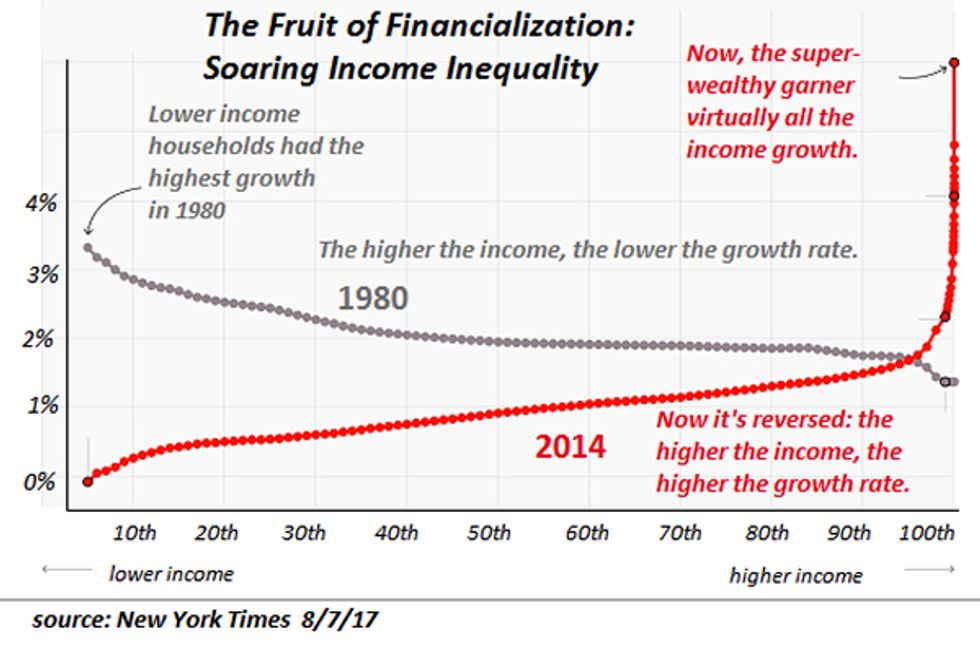
Famed financer Ray Dalio recently penned a commentary labeling the divergence of the wealthy elite from the bottom 90% The Most Important Economic, Political And Social Issue Of Our Time.
This is a topic many alt-financial bloggers have covered for years; I’ve penned dozens of essays on the topic, most recently The Fading Scent of the American Dream (October 16, 2017)
This chart depicts the inconvenient reality: central bank currency-creation-asset-buying has enriched the top of the wealth-power pyramid, with limited trickledown to the top 10% and negative effects on the bottom 90%.
The consequences of this outcome of central bank stimulus-for-the-already-wealthy can manifest in all sorts of ways.
Political pressure on central banks may grow, forcing policy changes or even limiting the scope of central bank largesse to banks and financiers.
Social movements demanding UBI and other income-distribution policies may become mainstream, a dynamic that as described above will add to the inflationary pressures building in the real world.
Once again, creating another trillion and buying more assets held by the wealthy won’t fix this problem—it will only make it worse.
Fragmentation of the Elites
As I have often noted, historian Michael Grant identified profound political disunity in the ruling class as a key cause of the dissolution of the Roman Empire. Grant described this dynamic in his excellent account The Fall of the Roman Empire, a book I have been recommending since 2009.
The chapter titles of the book provide a precis of the dynamics Grant identifies:
The Gulfs Between the Classes
The Credibility Gap
The Partnerships That Failed
The Groups That Opted Out
The Undermining of Effort
I’ve discussed profound political disunity in dozens of essays since 2009, for example, When Did Our Elites Become Self-Serving Parasites? (October 4, 2016)
The Real Trouble Begins When Rising Inequality Splinters the Elites (October 22, 2015)
There are a number of manifestations of profound political disunity we can discern:
-- The splintering of the technocrat class as soaring wealth and income inequality narrows opportunities for financial security for the class that considered security and wealth a birthright.
-- The fragmenting of the Deep State, the unelected, permanent leadership of the Establishment, a subject I’ve addressed since 2014: The Age of Disintegration: Political Disunity and Elites At War. (November 21, 2016)
-- The fragmentation of the two political parties into warring camps that have little common ground in a struggle for control of the rising tide of populism.
-- The splintering of the social order into conflicting classes of Haves and Have-Nots, a topic I covered in America's Nine Classes (April 13, 2015).
Once again, creating another trillion and buying assets—a policy that enriches the financial elites at the expense of every other class and elite—doesn’t solve the problem, it only makes it worse.
Popping the Everything Bubble Created by Central Bank Currency Creation-Asset Buying
As central bank creation of currency and asset purchases fail to solve the problems outlined above, these dynamics will undermine the status quo rather than prop it up. As central bank policies are increasingly fingered by the mainstream as the source of soaring wealth-income inequality, central bank policies supporting credit/asset bubbles will either be limited or cut off, and at that point all the credit/asset bubbles will pop.
In Part 2: What To Invest In When The Everything Bubble Bursts, we lay out our how to best prepare for the social discord, political disorder and financial upheaval that will result when the central banks inevitably lose control of the system.
As today's bubble-drunk asset prices start plummeting, what investment opportunities will offer the best returns?
To find out, click here to read Part 2 of this report (free executive summary, enrollment required for full access)
 Harold M. Lambert / Contributor | Getty Images
Harold M. Lambert / Contributor | Getty Images
 Adam Gray / Stringer | Getty Images
Adam Gray / Stringer | Getty Images Anadolu / Contributor | Getty Images
Anadolu / Contributor | Getty Images Brandon Bell / Staff | Getty Images
Brandon Bell / Staff | Getty Images