The saying "the worm has turned" refers to the moment when the downtrodden have finally had enough, and turn on their powerful oppressors.
The worms have finally turned against the privileged elites -- who have benefited so greatly from globalization, corruption, central bank stimulus and the profiteering of state-enforced cartels. It doesn’t matter as much as the punditry assumes whether they are turning Left or Right; the important thing is that the powerless have finally started challenging their privileged overlords.
Though the Powers That Be will attempt to placate or suppress the Revolt of the Powerless, the genies of political disunity and social disorder cannot be put back in the bottle. It took a generation of rising inequality, corruption and the erosion of opportunity to create a society of the protected (the haves) and the unprotected (the have-nots), and rubber-stamping more regulations and distributing Universal Basic Income (UBI) will not rebalance a system that is irrevocably out of balance.
But the rise of resistance, as yet nascent, is only half the story: economic trends and cycles are turning as well, and even if the worms remain passively underground, these reversals will disrupt the status quo. The dominant narrative--the rightness, goodness and sustainability of endless growth of consumption and debt--will unravel, and the internal contradictions of this New Gilded Age (widening wealth/income/power inequality) will finally burst through the thin façade of stability that’s been patched together over the past nine years of “recovery.”
Eight Key Trends/Cycles Are Turning
Here’s the thing about trends and cycles: when they inevitably lose altitude or reverse, we rush around trying to identify the cause. All sorts of theories are put forth, but as a general rule, it rarely boils down to one dynamic.
Consider the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire. Efforts to identify the cause go back hundreds of years, and include everything from barbarian invasions to the use of lead pipes to deliver water.
A new book, The Fate of Rome: Climate, Disease, and the End of an Empire, pins a significant part of the responsibility on climate change and pandemic diseases—system-wide dynamics that slowly sapped Rome’s vigor, food supplies, capital and labor force. Not only that, but cooling weather patterns in Eurasia may have been behind the westward movement of the mobile tribes (the Huns and Mongolians) that pushed existing tribes on Rome’s borders into Roman territories—the so-called Barbarian Invasions.
The point here is that systemic trends and cycles are often causally connected and tend to reinforce each other. This is how a stable, wealthy and resilient society gets hollowed out: trends end and cycles reverse, and forces that added stability, capital and resilience when they were working together are slowly replaced by forces that erode the foundations of wealth and stability.
In the current era, eight interconnected trends/cycles are either reaching the end of their run or reversing:
- Central bank distortion/manipulation of markets.
- The business cycle of credit/debt expansion and contraction.
- The yield/interest rate cycle.
- The commodity cycle.
- The stock market cycle.
- Regulation.
- Globalization.
- Demographics.
Each of these would need a short book to do the topic even partial justice, but let’s summarize each trend/cycle.
Let’s stipulate that technology isn’t a cycle or a trend; its disruptions of existing sectors and institutions accelerate and decelerate over time, but it is woven inseparably into all the trends and cycles listed above. That said, the emergence of some new technology doesn’t mean the business cycle will be repealed for all time; cycles and trends are influenced by Human Wetware V1.0, an OS developed between 100,000 and 160,000 years ago and still in Version One.
Resource depletion is another background to these trends and cycles: robots and drones will not restore depleted ground water or bring back ocean fisheries.
Central Bank Distortion / Manipulation of Markets
Minus the $21 trillion in central bank asset purchases and trillions more in liquidity/credit programs, would the global economy be growing and global markets be at nosebleed heights? We all know the answer is "no."
Central banks have engineered a "recovery" that looks real enough on the surface, but what are its foundations? Gamed statistics and manipulated markets—in other words, controlling not just the narrative but the information available to market participants. To achieve the desired outcome—rising equity markets, near-zero bond yields and incentivizing the purchase of risk-on assets—central banks have distorted market information and mechanisms.
The returns on this coordinated distortion are diminishing. The “buzz” from the initial injections has faded, and now that the monetary authorities are trying to wean the markets off of their drug, the markets have lost the ability to discover the price of assets, risk and capital on their own.
No wonder volatility is rising.
Flooding the economy with trillions in new stimulus worked wonders in the initial stage, but after 9 years, the unintended consequences are metastasizing.
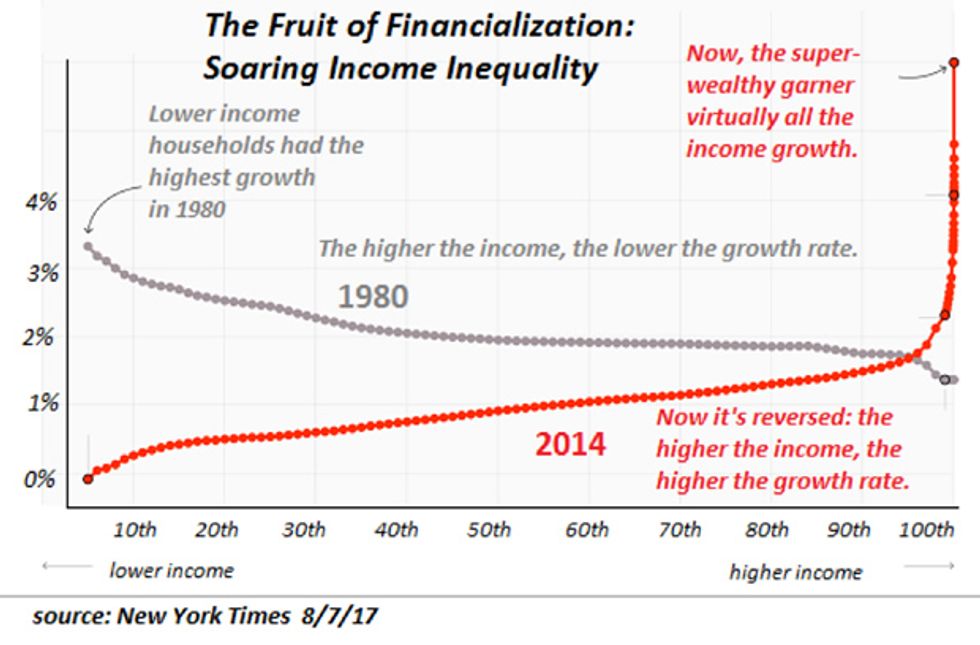
Goosing asset valuations higher in service of “the wealth effect” has widened wealth/ income inequality, creating a New Gilded Age of a few haves and many have-nots. The benefits of the central bank punch bowl—near-zero interest rates, leverage and access to unlimited credit--are reserved for those few at the top of the wealth-power pyramid; very little of the stupendous wealth created out of thin air has trickled down to the bottom 95%.
The relentless rise in asset valuations has pushed homes out of reach of those living in desirable urban/suburban markets, and exposed buyers to the risks of an inevitable reversion to the mean, i.e. a collapse of bubble prices back to historical norms.
Capital is not incentivized to invest in productivity or communities for the long haul; the incentives are for stock buybacks and short-term leveraged speculative bets, forms of mal-investment that hollow out the productive real economy is favor of a momentum-driven financialization boom.
Much of the political resistance troubling the status quo can be traced directly to central bank policies that have exacerbated the New Gilded Age inequalities and excesses. If the central banks can’t find the will to reduce their distortions in service of the few, the political will of the many will do it for them.
The Business Cycle of Credit Expansion & Contraction
The business cycle is a basic structure of any economy based on credit and flows of capital seeking the highest available returns at the lowest available risk. In the expansion stage, households and enterprises borrow more money to boost production and satisfy unmet demand. Speculators find opportunities in new enterprises and new markets.
In the contraction phase, all the inevitable excesses of freely available credit come home to roost. Marginal investments in new production fail to become profitable and go bust. Marginal household borrowers default, and speculators who bet the farm on momentum plays watch their capital evaporate like mist in Death Valley.
When too much income is being devoted to servicing existing debt, there’s no more net income available to support additional borrowing. Lenders facing losses due to defaults tighten lending standards, and credit—and thus the economy—contracts.
This cycle is an essential dynamic of capitalism. Central banks have attempted to eliminate the contraction phase that acts as the immune system, washing out bad debt and marginal borrowers. This has left the economy saddled with “zombie” corporations and debtors that would be liquidated if monetary policies weren’t enabling their feeble survival.
But even the most powerful central banks can’t force firms and individuals to borrow more money when it no longer makes sense to do so. And keeping zombie banks, corporations and households on life support weakens the financial system by piling up the equivalent of dead wood in the forest. When the inevitable conflagration of bad debt catches fire, many of the healthy trees will also be consumed in the flames.
The Yield / Interest Rate Cycle
Many observers are confident interest rates cannot rise due to the deflationary forces in play. Indeed, they predict a future decline in rates back to zero. Perhaps, but history suggests interest rates typically move in long cycles of roughly two or three decades. The current downtrend in rates dates back to 1981, which means the current trend is pushing 40 years. That’s stretching the historical boundaries.
As noted earlier, trends change and then we seek the causes. Interest rates are rising, and perhaps we need no explanation other than reversion to the mean.
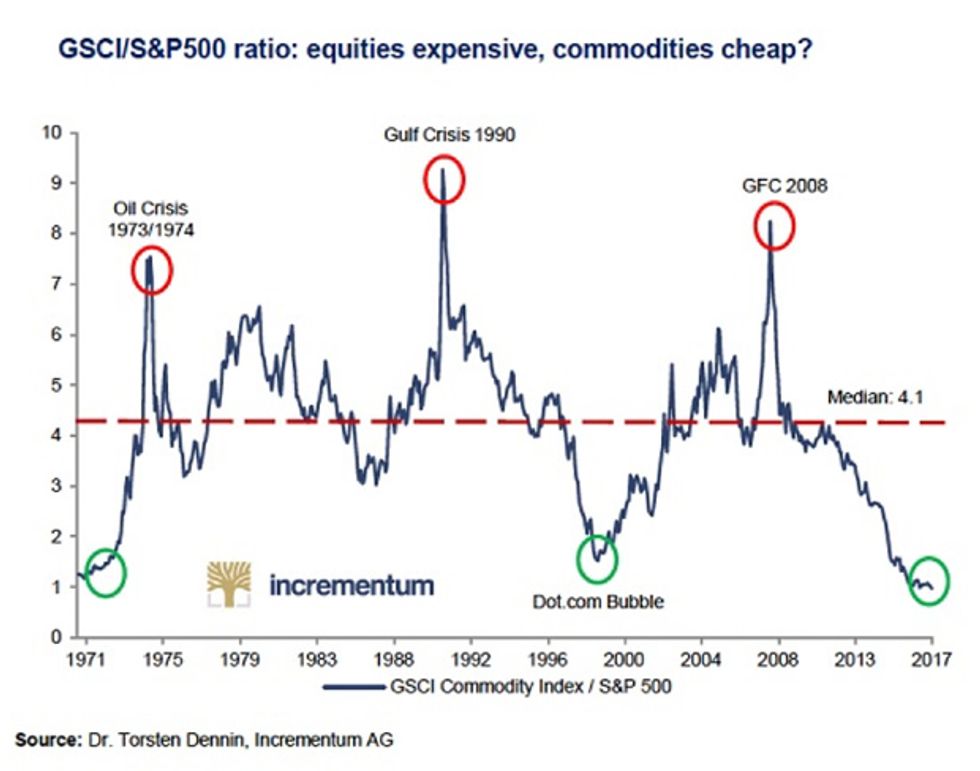
The Commodity Cycle
Compared to the stock market (the S&P 500), commodities are at their cyclical lows. As to what happens next, we need only look at a single chart, courtesy of Incrementum AG:
The Stock Market Cycle
We’re implicitly being told that stock markets can loft higher forever, as long as central banks are pumping out the financial stimulus. But nothing goes up forever; valuations get stretched, marginal buyers disappear and doubts about the continuing efficacy of central bank distortions creep in.
The typical Bull Market has a leading sector. Starting with the mass-market Industrial Revolution in the 19th century, leaders tend to be new industries: railroads, radio, computers, the Internet, etc., or existing industries that have been revolutionized by some innovation: for example, banks freed from regulatory oversight discovered subprime mortgages in the 2000s.
The current leaders—the so-called FAANG stocks—are getting tired. The tech leaders have reached a scale where growth must slow; the expansion of Facebook from 100 million users to 1 billion was a 10-fold increase; the expansion from 1 billion to 2 billion, a double. Are there even another billion potential users with the bandwidth, devices and interest to join? How much additional revenue can be extracted by selling the data of increasingly marginal users?
The same issues of scale are sapping the growth of Apple, Google, et al. What happens when Apple has already sold an iPhone to everyone with the means and interest to own one?
There is now political pushback against the quasi-monopolies of big tech. Politicians are being forced to “do something,” i.e. increase regulations, whether they accomplish the intended goal or not.
Valuations and profits are at the top of their respective cycles, the leaders are faltering, victims of their own dominance, and central banks are feeling pressured to reduce the punch bowl of free money for financiers.
Regulation
Democracy is no longer about solving real problems and being held accountable; it’s all about persuading the public that all is well, or distracting them with ginned up controversies. Incumbents get re-elected because they vacuum up enough campaign contributions to buy influence via the mass (corporate) media. They have little incentive to respond to voters, so they don’t.
What they can do is look like they’re doing something other than protecting the cartels and financiers that fund their permanent re-election campaigns. So they propose more regulations, most of which fail to achieve the desired results but succeed in burdening legitimate enterprises to the point of failure. Small enterprises simply fold up when the exhausted owners can no longer bear the burdens and corporations offshore everything that’s over-regulated.
The neoliberal ideology held that the many would benefit if regulations limiting enterprise were eased, and when done judiciously and with common sense, this has functioned as designed. But in the corrupt form of governance that dominates the global economy, regulatory capture means regulations protect cartels and insiders from competition. Insiders have rigged the system so they can punish competitors and let their cronies off the hook.
The useful regulations protecting the many from the exploitation of the few are being buried by counter-productive “do something” regulations and regulatory moats that protect cartels and insiders.
Globalization
Global trade has a long history, stretching back to the Bronze Age (1500 B.C.). Like every other market, it expands and contracts as conditions change. The emergence of China (and other nations) since the mid-1980s greatly expanded global trade and capital flows. This distributed new income and prosperity to hundreds of millions of people, and yet it also concentrated much of the newfound wealth in the hands of the few and left many behind.
Nothing goes up forever, not even globalization. Those left behind are starting to wonder if the good of globalization outweighs the costs.
Demographics
If high-population-growth Africa is set aside, the world’s working age populace is perched on the precipice of decline while the populace of retirees is exploding, not just in the developed world but in the developing world.
Although many put their hopes on robots generating unlimited wealth that will support the elderly and free the working age populace from labor, the more likely prospect is an economy that cannot fulfill the promises made to retirees back when the worker-retiree ratio was 10-to-1 and not the present-day 2-to-1.
Chris Hamilton has written three excellent explorations of demographics that cover the basics. The bottom line is the trend of rapidly-expanding workforces and modest numbers of dependent retirees has reversed:
- The Most Important Economic Charts...Aren't Economic Charts
- China's Booming Middle Class Set To Bust?
- Ultimate Indicator Suggests US Never Truly Recovered From the Great Financial Crisis
To underscore this point, chew on this sobering projection: in the US, for the first time ever, retirees will outnumber kids within just 20 years.
Time To Take Action
So as these 8 key trends and cycles change, what can we as individuals do?
In Part 2: 6 Essential Strategies For Prospering Through The Next Crisis, we detail specific steps to take with your money, your career, your lifestyle, your possessions and your mindset that will dramatically improve your odds of ending up on the winning side of these cycle reversals.
But time is of the essence. Preparation has value only if done in advance, and the turning point is upon us.
Click here to read Part 2 of this report (free executive summary, enrollment required for full access)

 USAF / Handout | Getty Images
USAF / Handout | Getty Images
 Bloomberg / Contributor | Getty Images
Bloomberg / Contributor | Getty Images David McNew / Stringer | Getty Images
David McNew / Stringer | Getty Images