Here are your democratic primary power rankings for candidates in the race. Can't wait to add Mike Gravel (to the top, obviously).
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Integer consequat suscipit mollis. Ut purus sapien, accumsan gravida augue a, facilisis posuere quam. In bibendum urna ac ligula efficitur condimentum. Phasellus rutrum est nec quam sodales, eget viverra lacus pulvinar. Maecenas non arcu sed nibh dignissim ultricies.
Morbi vitae justo at eros feugiat elementum sed interdum arcu. Donec id justo malesuada, molestie nisi in, pulvinar justo. Suspendisse faucibus, felis sed sodales pharetra, nisi lectus tristique lectus, eget posuere dolor ipsum eget felis. Cras sodales risus vitae lacinia volutpat. Nullam urna dui, feugiat id leo non, cursus auctor ipsum. Curabitur blandit, massa nec sollicitudin congue, massa leo faucibus mi, sit amet scelerisque nibh risus sed mauris. Fusce bibendum porttitor pellentesque.
Praesent posuere lectus vel augue pellentesque, ac euismod enim commodo. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae;
1.Bernie Sanders: 69.3 (Last Rank: 🔺1 | Last Score: 🔻69.3)
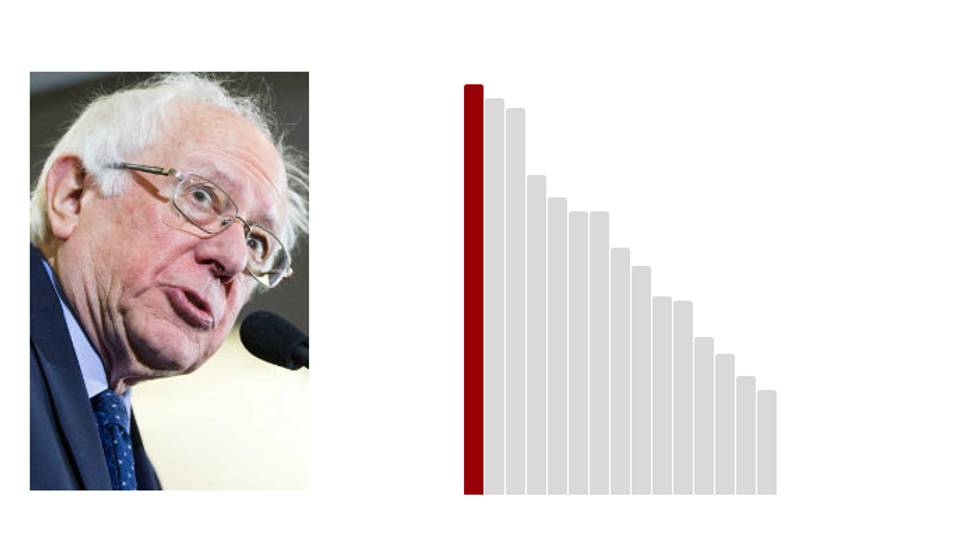
Bernie Sanders is serving his second term in the U.S. Senate after winning re-election in 2012 with 71 percent of the vote. His previous 16 years in the House of Representatives make him the longest serving independent member of Congress in American history. (Sanders.Senate.gov)
2.Kamala Harris: 66.8 (Last Rank: 🔺2 | Last Score: 🔻66.8)
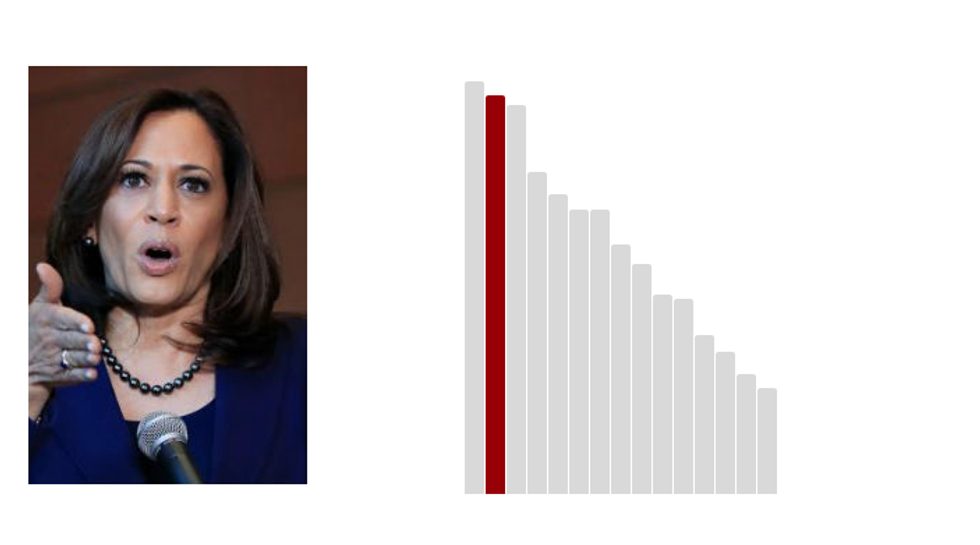
In 2017, Kamala D. Harris was sworn in as a United States Senator for California, the second African-American woman and first South Asian-American senator in history. She serves on the Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs Committee, the Select Committee on Intelligence, the Committee on the Judiciary, and the Committee on the Budget. (Harris.Senate.gov)
3.Beto O'Rourke: 65.2 (Last Rank: 🔺3 | Last Score: 🔻65.2)
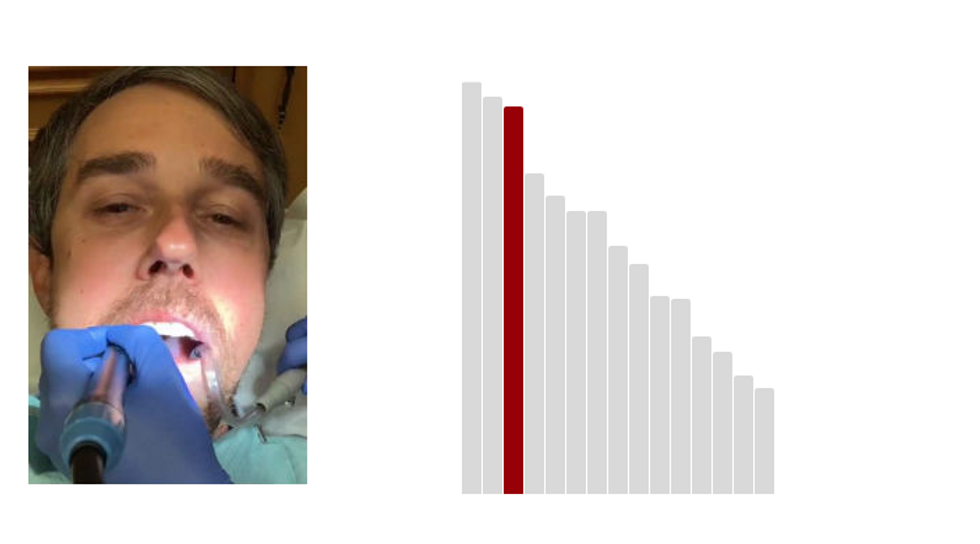
Beto O'Rourke, a Representative from Texas, was elected as a Democrat to the One Hundred Thirteenth and to the two succeeding Congresses (January 3, 2013-January 3, 2019). He was not a candidate for reelection to the One Hundred Sixteenth Congress in 2018, but was an unsuccessful candidate for election to the United States Senate. (Bioguide.Congress.gov)
4.Cory Booker: 54.0 (Last Rank: 🔺4 | Last Score: 🔻54.0)
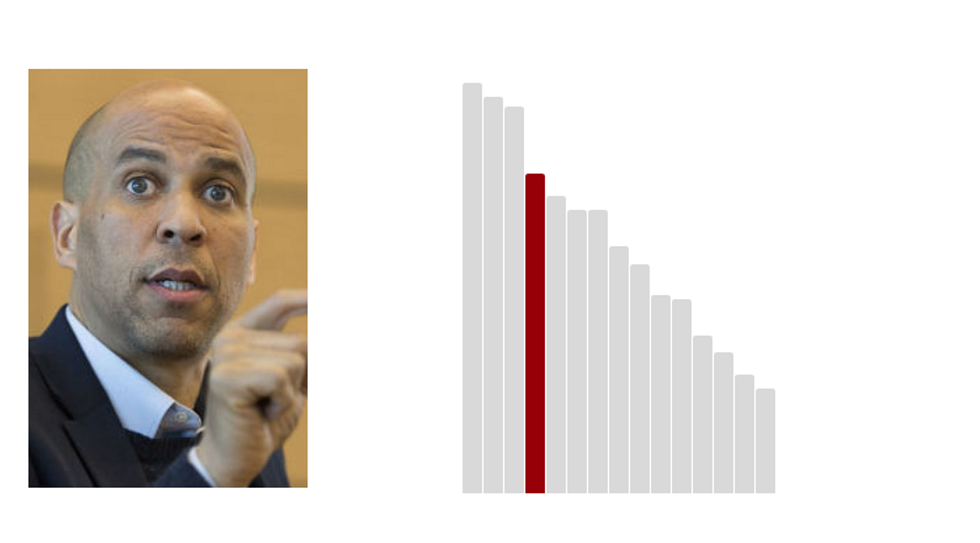
On October 16th, 2013, Booker won a special election to represent New Jersey in the United States Senate. On November 4th, 2014, Senator Booker was re-elected to a full six year term. As New Jersey's junior Senator, Cory Booker has brought an innovative and bipartisan approach to tackling some of the most difficult problems facing New Jersey and our country. (Booker.Senate.gov)
5.Amy Klobuchar: 50.2 (Last Rank: 🔺5 | Last Score: 🔻50.2)
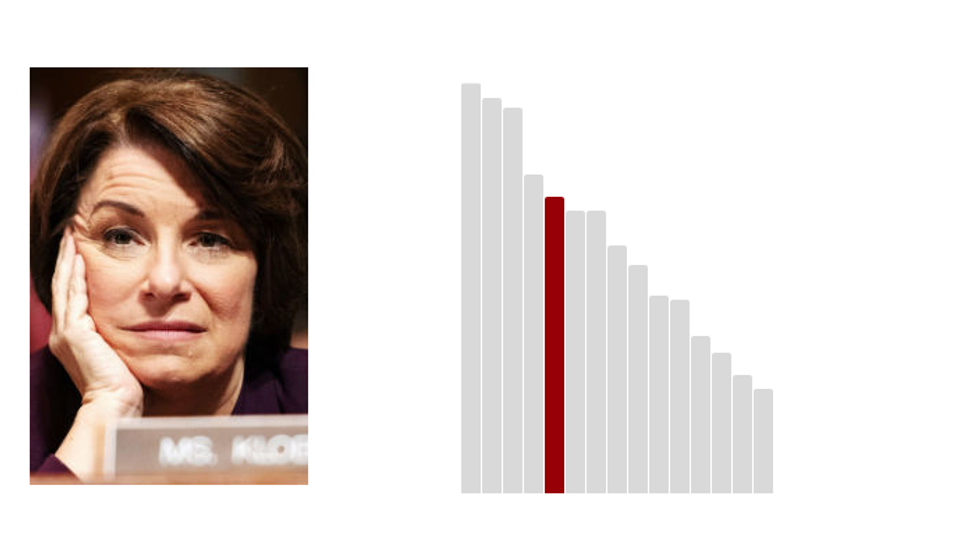
U.S. Senator Amy Klobuchar is the first woman elected to represent the State of Minnesota in the United States Senate. Throughout her public service, Senator Klobuchar has always embraced the values she learned growing up in Minnesota. (Klobuchar.Senate.gov)
6.Elizabeth Warren: 47.7 (Last Rank: 🔺6 | Last Score: 🔻47.7)
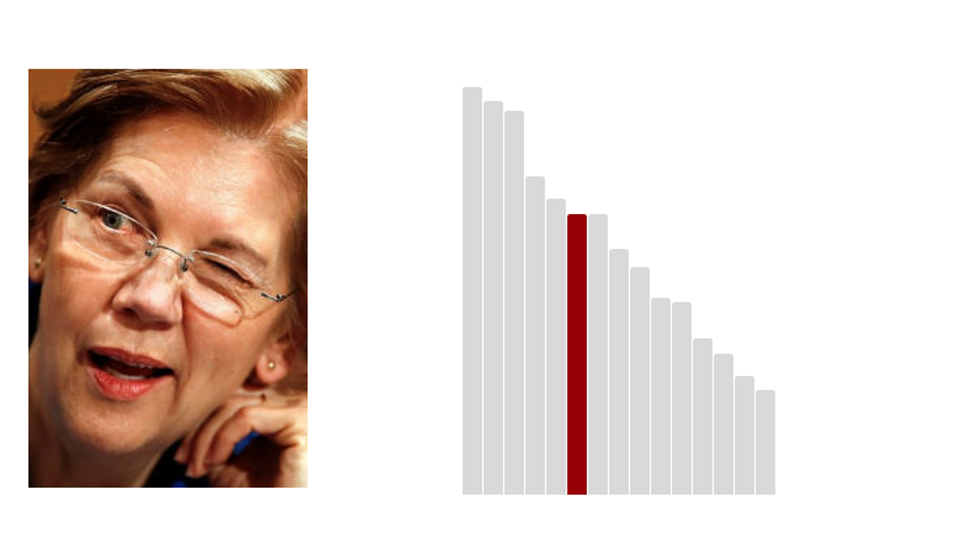
Elizabeth Warren, a fearless consumer advocate who has made her life's work the fight for middle class families, was elected to the United States Senate on November 6, 2012, by the people of Massachusetts. (Warren.Senate.gov)
7.Julian Castro: 41.8 (Last Rank: 🔺7 | Last Score: 🔻41.8)
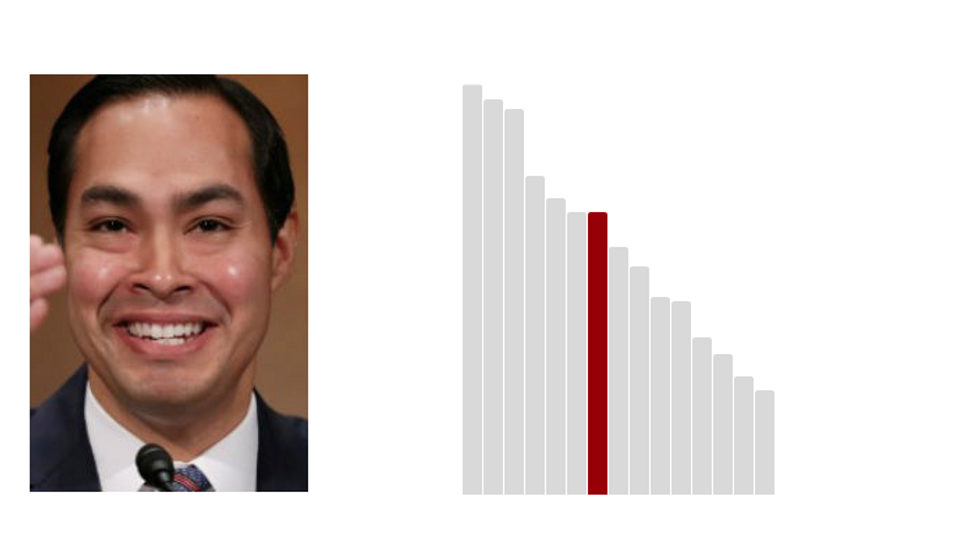
Julián Castro is an American Democratic politician who was the youngest member of President Obama's Cabinet, serving as the 16th United States Secretary of Housing and Urban Development from 2014 to 2017. (Wikipedia)
8.Kirsten Gillibrand: 38.7 (Last Rank: 🔺8 | Last Score: 🔻38.7)
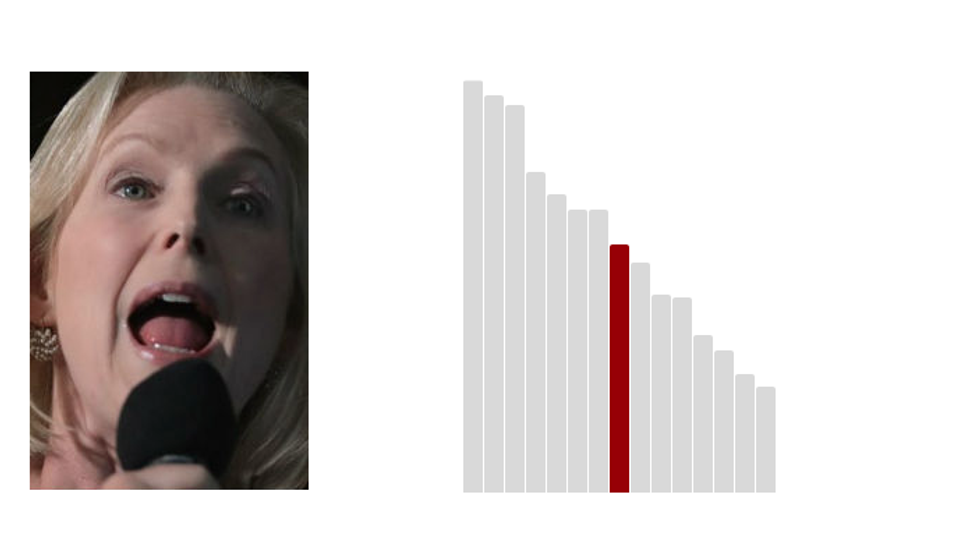
Kirsten Elizabeth Gillibrand is an American attorney and politician serving as the junior United States Senator from New York since 2009. A member of the Democratic Party, she previously served as a member of the U.S. House of Representatives from 2007 to 2009. (Wikipedia)
9.John Hickenlooper: 33.4 (Last Rank: 🔺9 | Last Score: 🔻33.4)
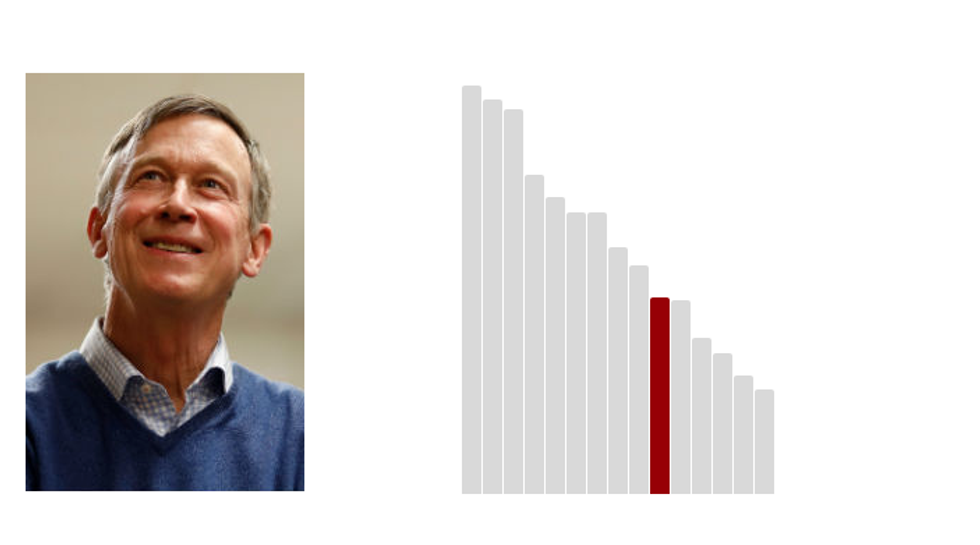
John Wright Hickenlooper Jr. is an American politician and businessman who served as the 42nd Governor of Colorado from 2011 to 2019. He is a member of the Democratic Party. (Wikipedia)
10.Jay Inslee: 32.8 (Last Rank: 🔺10 | Last Score: 🔻32.8)
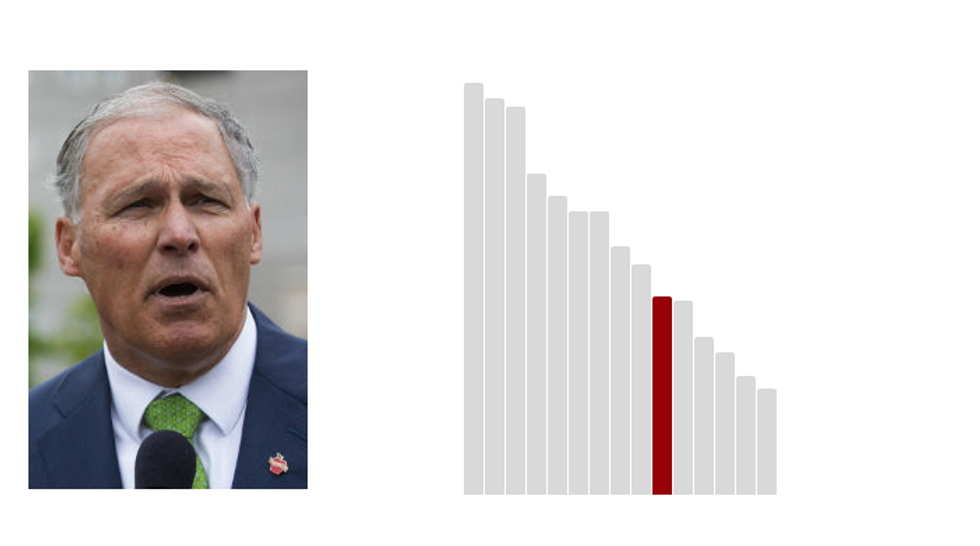
Jay Robert Inslee is an American politician, author and lawyer serving as the 23rd and current governor of Washington since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, he served in the United States House of Representatives from 1993 to 1995 and again from 1999 until 2012. (Wikipedia)
11.Pete Buttigieg: 31.1 (Last Rank: 🔺11 | Last Score: 🔻31.1)
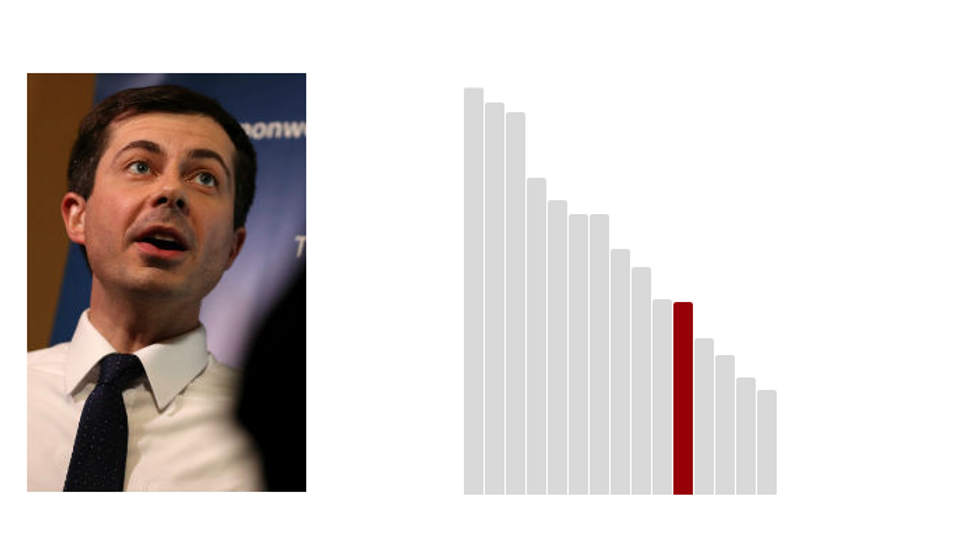
Peter Paul Montgomery Buttigieg is an American politician, serving since 2012 as the mayor of South Bend, Indiana as a member of the Democratic Party. He is also a lieutenant in the United States Navy Reserve. He was a consultant at McKinsey and Company, a management strategy consulting firm, from 2007 through 2010. (Wikipedia)
12.Tulsi Gabbard: 26.6 (Last Rank: 🔺12 | Last Score: 🔻26.6)
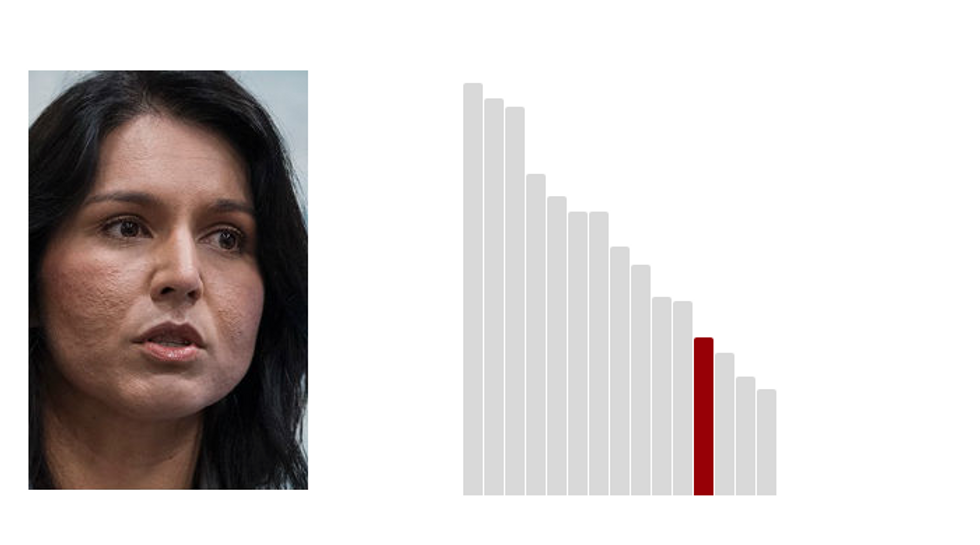
Tulsi Gabbard is an American politician serving as the U.S. Representative for Hawaii's 2nd congressional district since 2013. Following her election in 2012, she became the first Samoan American and the first Hindu member of the United States Congress. She is a member of the Democratic Party. (Wikipedia)
13.Andrew Yang: 23.9 (Last Rank: 🔺13 | Last Score: 🔻23.9)
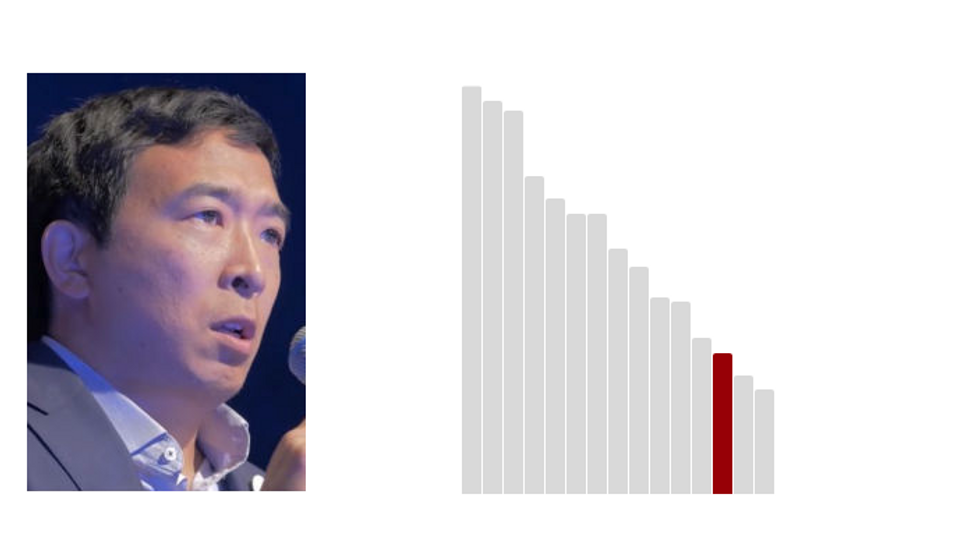
Andrew Yang is an American entrepreneur, the founder of Venture for America (VFA), and a U.S. 2020 Democratic presidential candidate. In Yang's bid for the 2020 presidential nomination, one of his main campaign goals is to implement a provision for Universal Basic Income (UBI) known as the Freedom Dividend for every American adult, in response to the rapid development of automation that is leading to workforce challenges. (Wikipedia)
14.John Delaney: 20.1 (Last Rank: 🔺14 | Last Score: 🔻20.1)
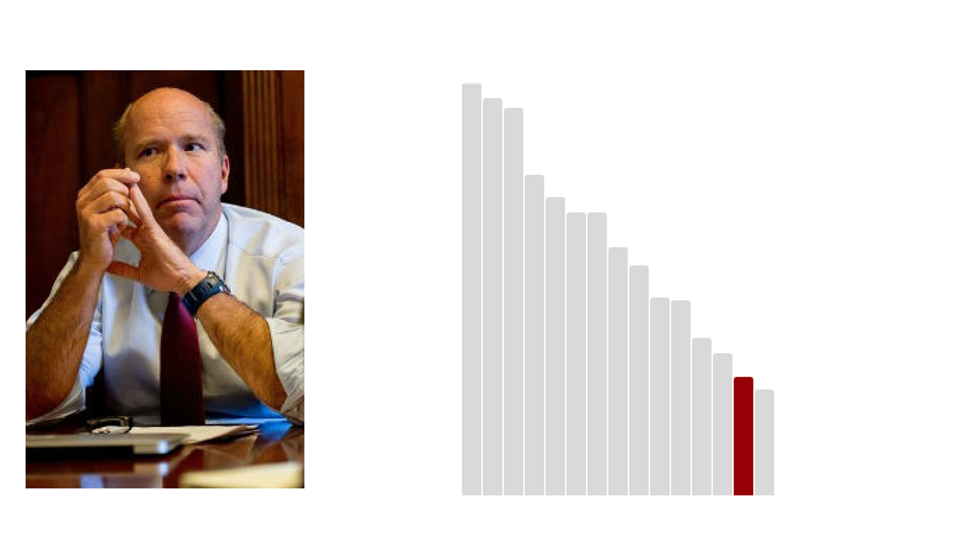

John Kevin Delaney is an American politician and businessman who is running for President of the United States in 2020. He was the United States Representative for Maryland's 6th congressional district from 2013 to 2019. He is a member of the Democratic Party. (Wikipedia)
15.Marianne Williamson: 17.8 (Last Rank: 🔺15 | Last Score: 🔻17.8)
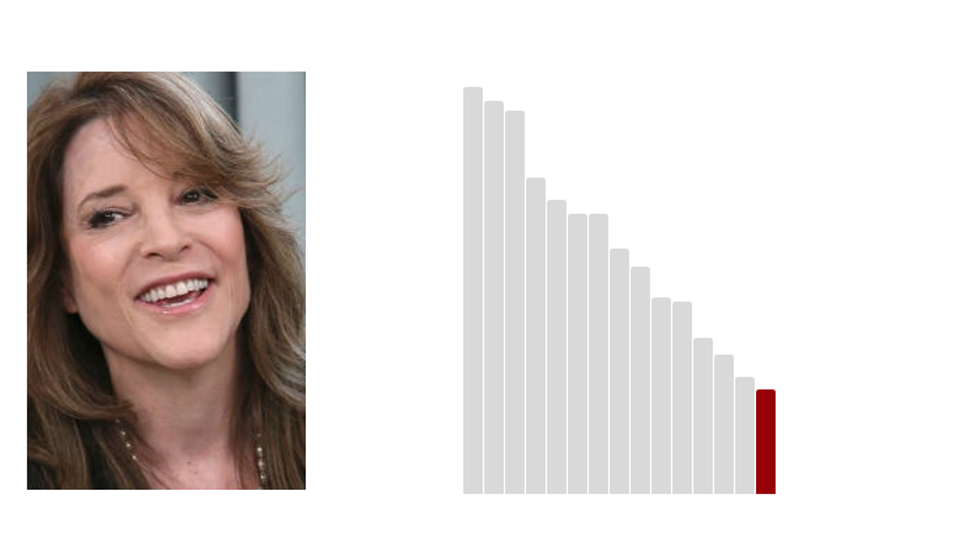
Marianne Deborah Williamson is an American spiritual teacher, author, lecturer, entrepreneur, and activist. She has written 13 books, including four New York Times number one bestsellers. She is the founder of Project Angel Food, a volunteer food delivery program that serves home-bound people with AIDS and other life-threatening illnesses. She is also the co-founder of The Peace Alliance, a nonprofit grassroots education and advocacy organization supporting peace-building projects. (Wikipedia)
 Brandon Bell / Staff | Getty Images
Brandon Bell / Staff | Getty Images
 Europa Press News / Contributor | Getty Images
Europa Press News / Contributor | Getty Images ANGELA WEISS / Contributor | Getty Images
ANGELA WEISS / Contributor | Getty Images Eric Lee / Stringer | Getty Images
Eric Lee / Stringer | Getty Images